Array Examples & ExceptionsJ8 Home « Array Examples & Exceptions
In the last lesson we looked at array manipulation using the Array object, in this lesson we continue our investigation of arrays by showing their usage through code examples and some of the exceptions that can occur when using them.
One Dimensional Array Examples Top
Lets look at some code to illustrate the use of one dimensional arrays:
package info.java8;
/*
One dimensional array examples
*/
public class OneDimensionArrays {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int intArray1[]; // Array declaration
intArray1 = new int[4]; // Array allocation
System.out.println("Value of position 4 (index 3) : " + intArray1[3]);
intArray1[3] = 672; // Array initialization
System.out.println("Value of position 4 (index 3) : " + intArray1[3]);
String[] strArray1;; // Array declaration
strArray1 = new String[3]; // Array allocation
System.out.println("Value of position 3 (index 2) : " + strArray1[2]);
strArray1[2] = "fred"; // Array initialization
System.out.println("Value of position 3 (index 2) : " + strArray1[2]);
String strArray2[] = {"one", "aa", "c", "rt", "je"}; // Single statement array creation
System.out.println("Value of position 5 (index 4) : " + strArray2[4]);
}
}
Running the OneDimensionArrays class produces the following output:
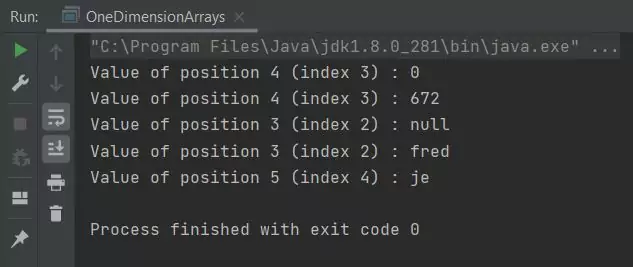
OneDimensionArrays class.You should see 5 lines of output as in the screenshot above. This is is our first look at the new operator which tells the compiler to construct a new instance of the object in question. We use the zero-based index
number of the array object to access elements within the array. We are printing an element of the array after the allocation step to show default initialization and the same element after we have initialized it. The last line
of output displays an element after a single statement array creation step.
Two Dimensional Array Examples Top
Lets look at some code to illustrate the use of two dimensional arrays:
package info.java8;
/*
Two dimensional array examples
*/
public class TwoDimensionArrays {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int intArray1[][]; // Array declaration
intArray1 = new int[3][4]; // Array allocation
for (int i=0; i<intArray1.length; i++) { // Array initialization using a for loop
for (int j=0; j<intArray1[i].length; j++) {
intArray1[i][j] = i + j;
System.out.println("Array position: " + i + ":" + j + " = " + intArray1[i][j]);
}
}
// Single statement array creation
int[][] intArray2 = new int[][]{ {5, 33}, {0}, {5, 4, 71} }; // Irregular array
for (int i=0; i<intArray2.length; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<intArray2[i].length; j++) {
System.out.println("Array2 position: " + i + ":" + j + " = " + intArray2[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
Running the TwoDimensionArrays class produces the following output:
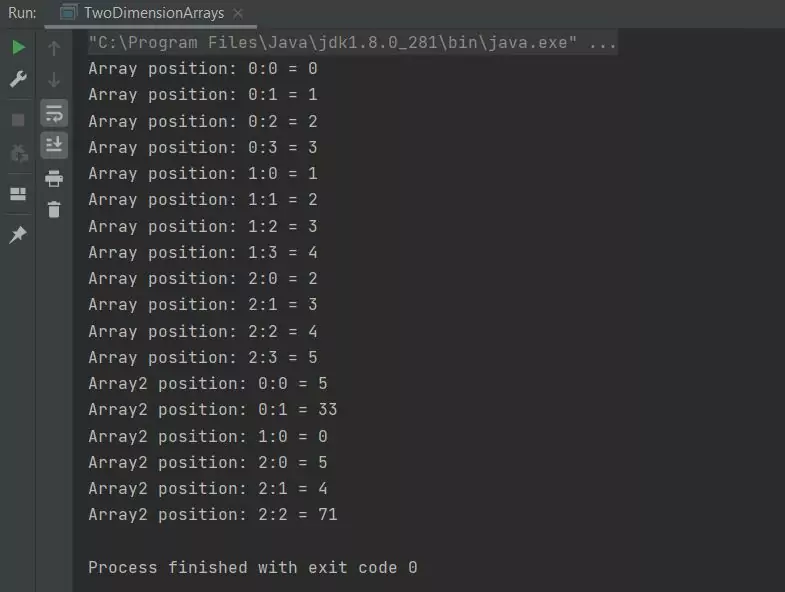
TwoDimensionArrays class.The above screenshot shows the output of a couple of two-dimensional arrays. The first regular array is created using multiple statements and initialized using two for loops; we print the elements as we initialize
them. The second irregular array is created using a single statement; we then use a couple of for loops to cycle through the array printing out the element values. We are using the anArray.length
code to form the loop iteration. Each array has a length variable associated with it and because arrays are zero-index based this is a perfect way of looping through all
the elements of an array.
java.lang Array Exceptions Top
As mentioned in the Getting Started lesson all our programs implicitly import the java.lang Package. Within this package are classes of exceptions we talk about in great detail in the Exceptions section of the site. For now we are purely interested in those exceptions that can be thrown by our arrays.
NegativeArrayCreation Exception Top
Following is example code and a screenshot of the runtime error when trying to access an array with a negative array allocation:
package info.java8;
/*
Negative array creation
*/
public class NegativeArrayCreation {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int negativeArray[]; // Array declaration
negativeArray = new int[-2]; // Negative array allocation
negativeArray[0] = 672; // Array initialization
}
}
Running the NegativeArrayCreation class produces the following output:
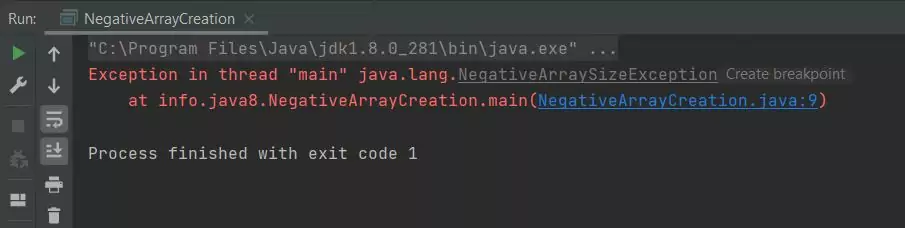
NegativeArrayCreation class.As you can see when we try to run the NegativeArrayCreation class we get a NegativeArraySizeException exception.
ArrayOutOfBoundsException Exception Top
Following is example code and a screenshot of the runtime error when trying to access an array element outside the allocation for that array:
package info.java8;
/*
Out of bounds example
*/
public class OutOfBoundsArray {
public static void main (String[] args) {
String strArray[] = {"one", "aa"}; // Single statement array creation
System.out.println("Position 3 (index 2) : " + strArray[2]); // Access outside allocation
}
}
Running the OutOfBoundsArray class produces the following output:
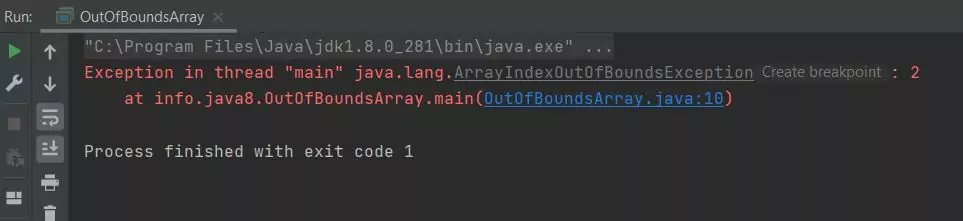
OutOfBoundsArray class.As you can see when we try to run the OutOfBoundsArray class we get an ArrayOutOfBoundsException exception as we are trying to access an index outside the bounds of the array.
ArrayStoreException Exception Top
Following is example code and a screenshot of the runtime error when trying to store an invalid type into an array:
package info.java8;
/*
Invalid type example
*/
public class StoreArrayCreation {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Number[] anArray = new Float[1]; // Array declaration
anArray[0] = new Integer(1); // Invalid type
}
}
Running the StoreArrayCreation class produces the following output:
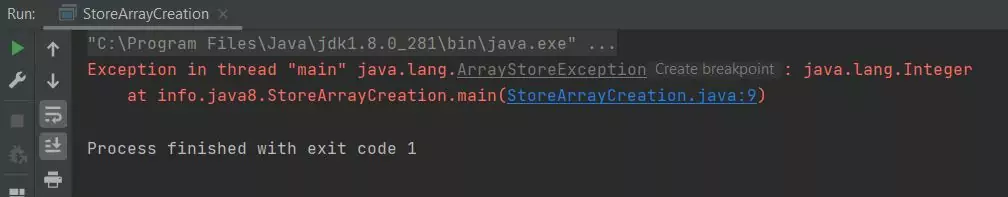
StoreArrayCreation class.As you can see when we try to run the StoreArrayCreation class we get an ArrayStoreException exception as an Integer object is an invalid type for this Float object array.
Related Quiz
Objects & Classes Quiz 2 - Array Examples & Exceptions
Lesson 2 Complete
In this lesson we looked at some examples of using Array objects and some exceptions that can happen when using them.
What's Next?
In the next lesson we look at class structure and syntax within our Java programs.