Bounded Wildcard TypesJ8 Home « Bounded Wildcard Types
We saw how we can use Bounded Types to get around the problem with invariance and we then looked at how to allow an unknown type by using Unbounded Wildcard Types in the previous two lessons. What if we had a scenario where we only want a method to work on a particular class or subclasses of it? For this type of situation we can use bounded wildcard types to only allow certain classes to use a method.
Ok, lets start by creating and building some simple classes:
package info.java8;
public class A {
{
System.out.println("A Object initializer");
}
}
package info.java8;
public class B extends A {
{
System.out.println("B Object initializer");
}
}
package info.java8;
public class C extends B {
{
System.out.println("C Object initializer");
}
}
package info.java8;
public class D { // Nothing to do with other classes
{
System.out.println("D Object initializer");
}
}
Build the classes in the usual way.
Now we need to write a simple generic class that will take any type and have a method within in that will eventually only work on the A class and subclasses of it but first we will let
the method work with any type:
package info.java8;
/*
Simple generic class that accepts any object
*/
public class BoundedWildcardType<T> {
// Generic object declaration
private final T genericObj;
// Pass reference to object of type T to our constructor
public BoundedWildcardType(T genericObj) {
this.genericObj = genericObj;
}
// Output object type of BoundedWildcardType to console
public void showObjectType(BoundedWildcardType<T> obj) {
System.out.println("Object type of BoundedWildcardType is " + genericObj.getClass().getName());
}
}
Building the BoundedWildcardType class produces the following output:
BoundedWildcardType class.Now we need to write a test class to show how we can pass various objects to our BoundedWildcardType class:
package info.java8;
/*
Test our BoundedWildcardType class that accepts any object
*/
public class TestBoundedWildcardType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create some objects
A a = new A();
B b = new B();
C c = new C();
D d = new D();
// Test the BoundedWildcardType using A, B, C and D objects
BoundedWildcardType<A> genAObj = new BoundedWildcardType<>(a);
genAObj.showObjectType(genAObj);
BoundedWildcardType<B> genBObj = new BoundedWildcardType<>(b);
genBObj.showObjectType(genBObj);
BoundedWildcardType<C> genCObj = new BoundedWildcardType<>(c);
genCObj.showObjectType(genCObj);
BoundedWildcardType<D> genDObj = new BoundedWildcardType<>(d);
genDObj.showObjectType(genDObj);
}
}
Running the TestBoundedWildcardType class produces the following output:
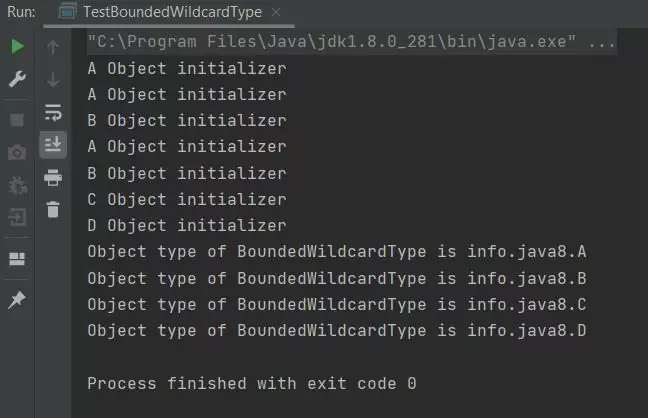
TestBoundedWildcardType class.Well nothing new here, all the classes run as expected. Now we want to change the BoundedWildcardType class so that only objects of type A or sublasses thereof can use the
showObjectType(BoundedWildcardType obj) method and for this we need a bounded wildcard type.
Change the signature to showObjectType(BoundedWildcardType<? extends A> obj) as shown below and rebuild the BoundedWildcardType class.
package info.java8;
/*
Simple generic class that accepts any object
*/
public class BoundedWildcardType<T> {
// Generic object declaration
private final T genericObj;
// Pass reference to object of type T to our constructor
public BoundedWildcardType(T genericObj) {
this.genericObj = genericObj;
}
// Output object type of BoundedWildcardType to console
public void showObjectType(BoundedWildcardType<? extends A> obj) { // Changed to bounded wild card type
System.out.println("Object type of BoundedWildcardType is " + genericObj.getClass().getName());
}
}
Rebuilding the TestBoundedWildcardType class after the amendments produces the following output:
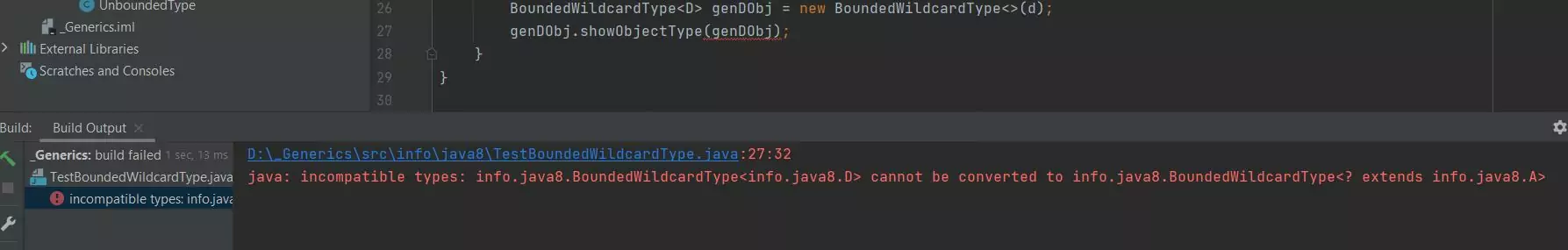
TestBoundedWildcardType class after the amendments .As you can see from the screenshot above the compiler won't allow us to call the showObjectType(BoundedWildcardType<? extends A> obj) method with an object of class D because
the method now has an unbounded wildcard type that only allows the A class and its subclasses.
Remove the creation and call for the genDObj in the TestBoundedType class for the class D type as shown below and rebuild the TestBoundedType class.
package info.java8;
/*
Test our BoundedWildcardType class that accepts any object
*/
public class TestBoundedWildcardType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create some objects
A a = new A();
B b = new B();
C c = new C();
// Test the BoundedWildcardType using A, B, and C objects
BoundedWildcardType<A> genAObj = new BoundedWildcardType<>(a);
genAObj.showObjectType(genAObj);
BoundedWildcardType<B> genBObj = new BoundedWildcardType<>(b);
genBObj.showObjectType(genBObj);
BoundedWildcardType<C> genCObj = new BoundedWildcardType<>(c);
genCObj.showObjectType(genCObj);
}
}
Rerunning the TestBoundedWildcardType class after the amendments produces the following output:

TestBoundedWildcardType class after the amendments.Related Quiz
Generics Quiz 7 - Bounded Wildcard Types Quiz
Lesson 7 Complete
In this lesson we looked at generic bounded wild card types and how to use them.
What's Next?
In the next lesson we look at generic methods.